Refractory stainless steel anchors have a wide range of application fields due to their excellent properties:
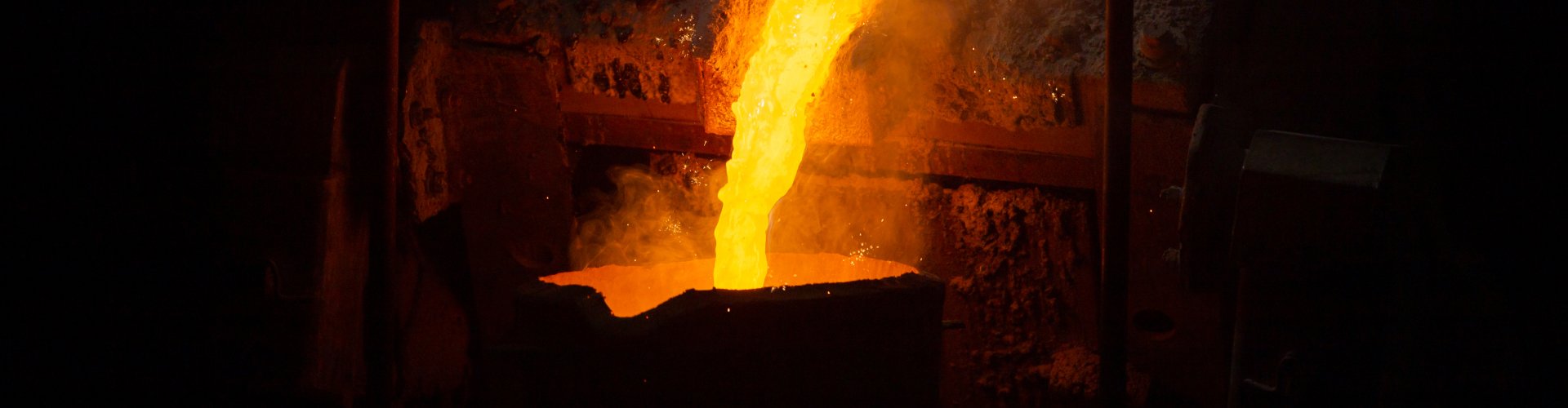
Metallurgical Industry: In steel mills and non-ferrous metal smelting plants, these anchors are used to fix refractory linings in furnaces and kilns. They can withstand the high temperatures and corrosive atmospheres generated during the smelting process, ensuring the stability of the refractory structure and preventing the lining from falling off, thus maintaining the normal operation of the equipment.
Power Generation Industry: In coal-fired power plants, especially in boilers, refractory stainless steel anchors play a crucial role in fixing refractory materials in the combustion chamber and flue. They help to resist the erosion of high-temperature flue gas and ash, and ensure the effective insulation and heat retention of the boiler, improving the thermal efficiency of power generation.
Glass Industry: In glass melting furnaces, these anchors are applied to fix refractory bricks and linings. They can endure the high temperatures and chemical erosion of the molten glass environment, maintaining the integrity of the furnace structure and ensuring the stable quality of glass production.
Ceramic Industry: During the firing process of ceramics in kilns, refractory stainless steel anchors are used to fix refractory components. They can maintain their mechanical properties in a high-temperature environment, ensuring the stability of the kiln structure and facilitating the uniform heating of ceramic products, which is beneficial to improving the quality of ceramics.
Petrochemical Industry: In petrochemical plants, these anchors are used to fix refractory materials in reactors and furnaces. They can resist the corrosion of various chemical substances and high temperatures, ensuring the safe and stable operation of equipment in the petrochemical production process.
Incineration Industry: In waste incinerators, refractory stainless steel anchors are used to fix refractory linings. They can withstand the high temperatures and corrosive gases generated during waste incineration, protecting the metal shell of the incinerator and extending the service life of the equipment.